ann_elucubrations
Sorting my notes about artificial neural networks
Plant identification
In control systems, a plant is usually modeled by an ordinary differential equation
where is the state of the system and is its input
When working with digital systems, it is common practice to discretize the above continuous-time model by considering the input to be constant on the time interval and use a difference equation like
As a universal function approximator, an Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) can be trained to approximate the plant’s dynamics.
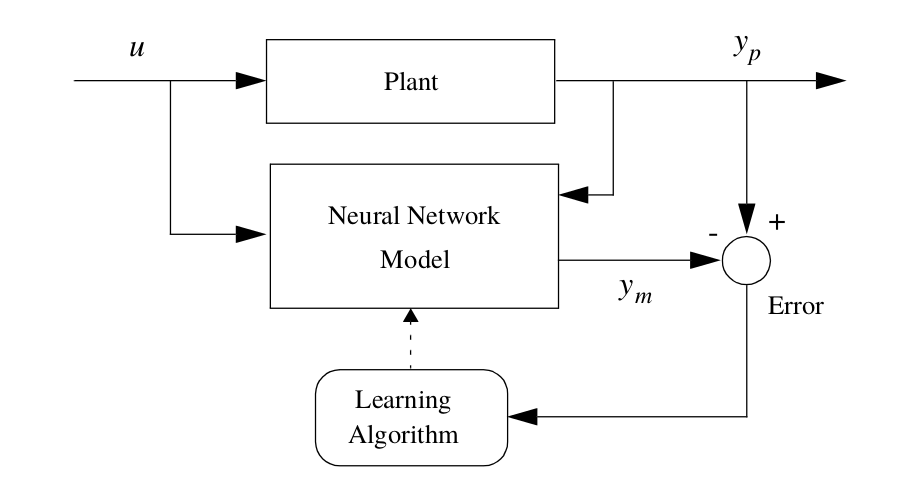
Input/Output identification
NARMA model
Control-Affine model